Adding Model Classes
In Solution Explorer, right click the Models folder, select Add, and then select Class.
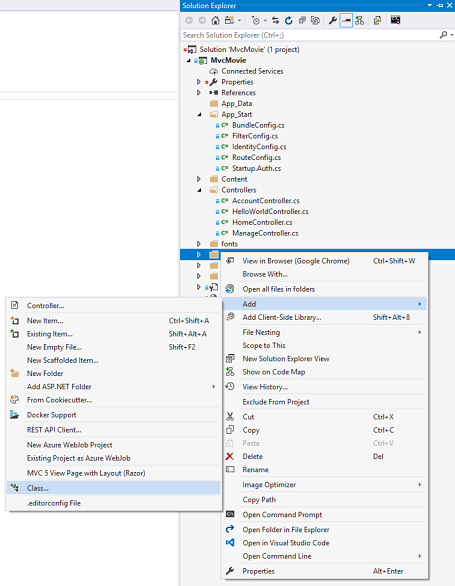
Enter the class name "Movie".
Add the following five properties to the
Movie class:
C#
using System;
namespace MvcMovie.Models
{
public class Movie
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public DateTime ReleaseDate { get; set; }
public string Genre { get; set; }
public decimal Price { get; set; }
}
}
We'll use the
Movie class to represent movies in a database. Each instance of a Movie object will correspond to a row within a database table, and each property of the Movie class will map to a column in the table.1
Note: In order to use System.Data.Entity, and the related class, you need to install the Entity Framework NuGet Package. Follow the link for further instructions.
In the same file, add the following
MovieDBContext class:4
C#
using System;
using System.Data.Entity;
namespace MvcMovie.Models
{
public class Movie
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public DateTime ReleaseDate { get; set; }
public string Genre { get; set; }
public decimal Price { get; set; }
}
public class MovieDBContext : DbContext
{
public DbSet<Movie> Movies { get; set; }
}
}
The
MovieDBContext class represents the Entity Framework movie database context, which handles fetching, storing, and updating Movie class instances in a database. The MovieDBContext derives from the DbContext base class provided by the Entity Framework.
In order to be able to reference
DbContext and DbSet, you need to add the following using statement at the top of the file:1
C#
using System.Data.Entity;
You can do this by manually adding the using statement, or you can hover over the red squiggly lines, click
Show potential fixes and click using System.Data.Entity;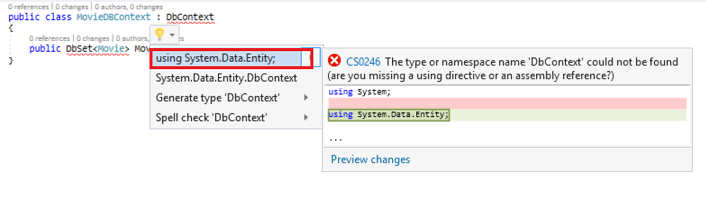
Note: Several unused
using statements have been removed. Visual Studio will show unused dependencies as gray. You can remove unnused dependencies by hovering over the gray dependencies, click Show potential fixes and click Remove Unused Usings.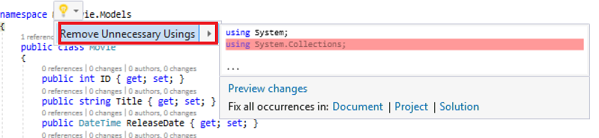
Comments
Post a Comment